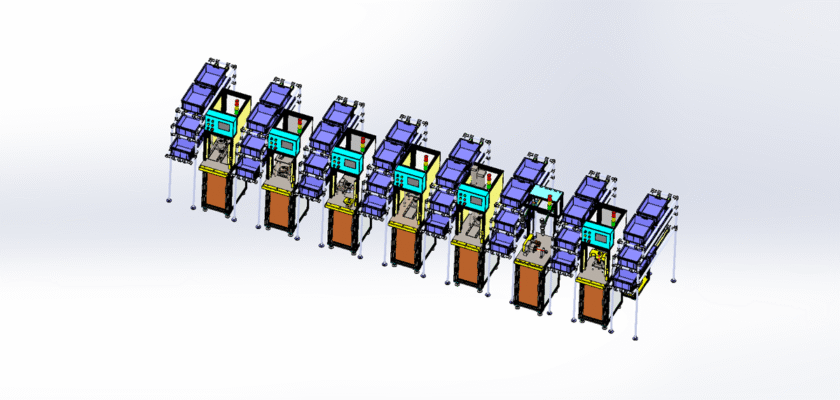
A switch assembly line is a highly specialized manufacturing system designed to automate the process of assembling electrical switches. This critical piece of equipment plays a vital role in industries ranging from consumer electronics and automotive manufacturing to industrial control and home appliances. By integrating a series of automated workstations, a switch assembly line can significantly increase production speed, reduce labor costs, and, most importantly, ensure a consistent level of quality that’s difficult to achieve with manual assembly. Our free CAD drawing provides a detailed overview of a typical switch assembly line, giving you a valuable resource to understand the mechanics, design, and flow of an automated production system.
The line operates by breaking down the complex task of switch assembly into a sequence of smaller, manageable steps. These steps are performed by various automated components like robotic arms, which are used for picking and placing tiny parts with extreme precision; vibratory bowl feeders, which orient components for easy assembly; and conveyor systems, which transport the partially assembled switches from one station to the next. The entire process is managed by a central control system, often a Programmable Logic Controller (PLC), which synchronizes the movements and operations of each station. This meticulous control ensures that every switch is assembled correctly and consistently, meeting the strict quality and safety standards required for electrical components.
Key Features:
- High-Speed Production: Automates repetitive tasks to achieve a much faster production rate than manual assembly.
- Superior Quality Control: Minimizes human error, ensuring each switch is assembled to precise specifications and reducing the number of defective units.
- Modular Design: The line is often designed in a modular fashion, allowing for easy reconfiguration to accommodate different switch types and production volumes.
- Increased Safety: Removes human workers from repetitive or hazardous tasks, improving workplace safety.
- Integrated Testing: Can include automated testing and inspection stations to verify electrical continuity and functionality throughout the assembly process.